Institute of Biomedical Research and InnovationDepartment of Infectious Disease Research
NEWS
-
06.05.2025
-
The article “Heat shock protein 90 chaperone activity is required for hepatitis A virus replication.”
was published in Journal of Virology.
A researcher / Research focus
We aim to study pathogenesis of infectious diseases to develop diagnosis and treatment methods.
The WHO estimates that there are more than 300 million people who are infected with the hepatitis virus all over the world. Hepatitis virus infection contributes to onset of cirrhosis and liver cancer, killing more than 1 million people each year. Japan is no exception to this situation, and hepatitis virus infection has become a serious public health problem. Our department attempts to investigate how the hepatitis virus can persist in hepatocytes and cause cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. By making a full investigation of the mechanism for enabling the sustained infection of the virus in hepatocytes and subsequent onset of the disease, we will explore clues for the development of methods for eliminating the virus, predicting its severity and preventing the progression of the disease.

Professor
Visiting Professor of Kobe UniversityMasamichi MuramatsuE-mail:muramatsu★fbri.org
(Replace ★ with @)
Lab Member
Masamichi Muramatsu, MD, PhD, Professor
Tomoyuki Shiota PhD, Research Assistant Professor
Itoe Shiota PhD, Research Associate
Yuko Sasaki, Technical staff
Manami Yamaoka, Technical staff


- Research focus
- Publications
This is a new research department established in 2021. Currently, we are in the process of setting up a laboratory.
We will update information on our website as we make progress in research and obtain achievement.
In Japan, the hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus are the two major hepatitis viruses that cause cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus are viruses that have DNA and RNA in their genomes, respectively, and are virologically different viruses. For the latter virus, which is the hepatitis C virus, several very good antiviral agents have been put into practical use in the last 10 years, and it has become a realistic goal to eliminate the virus from the liver. For the former virus, which is the hepatitis B virus, on the other hand, reverse transcription inhibitors are generally used as antiviral agents. The 2012 discovery of a receptor essential for the hepatitis B virus to infect cells has led to a rapid understanding of the viral life cycle in hepatocytes, especially understanding of the entry process of the hepatitis B virus into hepatocytes. Based on this basic information, drugs that block the invasion of viruses have been developed and are being used for treatment.
The hepatitis B virus is able to contain double-stranded covalently closed circular DNA called cccDNA in the nucleus of hepatocytes (Fig. 1). Although reverse transcriptase inhibitors are very good antiviral agents, they cannot eliminate cccDNA from infected hepatocytes once they have been generated, and if treatment is interrupted, the virus may be reproduced, starting from the cccDNA. New entry inhibitors also have the same weaknesses. Therefore, how to control cccDNA is extremely important for elimination of the virus from the body, and it is a major issue for the development of new antiviral agents.
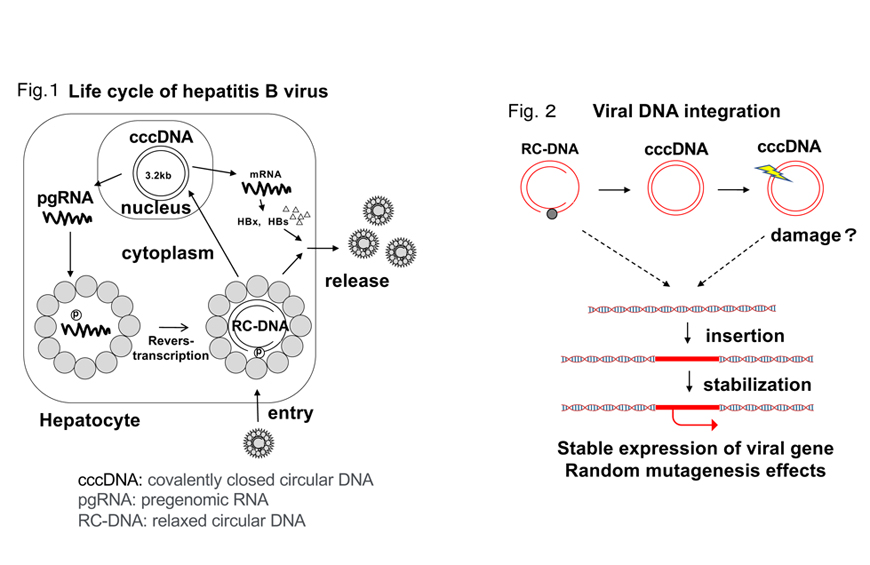
This phenomenon is currently assumed to be caused by partially single-stranded viral DNA (RC-DNA) formed after reverse transcription or damaged cccDNA integrated into the host genome by some mechanism and stabilized.
The hepatitis B virus has genes (HBx, etc.) that have been suggested to have carcinogenic activity. It is assumed that constitutive expression of viral oncogenes from these genomic loci in which the oncogene is inserted promotes oncogenic transformation.
In our department, we will study how cccDNA lurks in hepatocytes and how viral genome insertion occurs and causes hepatocytes to become cancerous. Based on the basic information obtained, we will attempt to find clues for the development of new diagnostic methods and therapeutic agents.
Besides themes such as cccDNA and viral genome insertion, we plan to engage in research on various infectious pathologies. This department has just been launched, and we appreciate your assistance and support.
Publications
2025
- Heat shock protein 90 chaperone activity is required for hepatitis A virus replication.
Li Y, Zheng X, Xie L, Kapustina M, Shirasaki T, Yonish B, Chen X, Hirai-Yuki A, Nagata N, Suzuki R, Isogawa M, Vogt MR, Muramatsu M(#), Lemon SM(#). J Virol. 2025 Jun 5:e0050225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00502-25. Online ahead of print.PMID: 40470959.
(#): corresponding authors - RXR agonist S169 inhibits HBV/HDV entry in vitro by disrupting KIF4-dependent NTCP trafficking. Sameh A. Gad, Doaa A. Abo Elwafa, Saied A. Hussein, Kento Fukano, Takanobu Kato, Ikuo Shoji, Kazuaki Chayama, Masamichi Muramatsu, Masanori Isogawa, Takaji Wakita, Daniel Merk, HusseinH.Aly. Antiviral Research. Available online 14 June 2025, 106214.
- Prediction of cccDNA dynamics in hepatitis B patients by a combination of serum surrogate markers.
Kwang Su Kim, Masashi Iwamoto, Kosaku Kitagawa, Hyeongki Park, Sanae Hayashi, Senko Tsukuda, Takeshi Matsui, Masanori Atsukawa, Kentaro Matsuura, Natthaya Chuaypen, Pisit Tangkijvanich, Lena Allweiss, Takara Nishiyama, Naotoshi Nakamura, Yasuhisa Fujita, Eiryo Kawakami, Shinji Nakaoka, Masamichi Muramatsu, Kazuyuki Aihara, Takaji Wakita, Alan S Perelson, Maura Dandri, Koichi Watashi, Shingo Iwami, Yasuhito Tanaka. PLoS Comput Biol
. 2025 Jan 9;21(1):e1012615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012615. eCollection 2025 Jan.
2024
- Persistent Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Epithelial Cells Leads to APOBEC3C Expression and Induces Mitochondrial DNA Mutations.
Aung Phyo Wai, Richardo Timmy, Kousho Wakae, Shunpei Okada, Masamichi Muramatsu, Hironori Yoshiyama, Hisashi Iizasa. Microbiol Immunol. 2024 Dec 20.doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13196. - Structural basis for hepatitis B virus restriction by a viral receptor homologue.
Shionoya K, Park JH, Ekimoto T, Junko ST, Mifune J, Morita T, Ishimoto N, Umezawa H, Yamamoto K, Kobayashi C, Kusunoki A, Nomura N, Iwata S, Muramatsu M, Tame JRH, Ikeguchi M, Park SY, Watashi K. Nat Commun. 15(1):9241. 2024. Doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53533-6. - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 gapmer antisense oligonucleotides targeting the main protease region of viral RNA.
Yamasaki M, Saso W, Yamamoto T, Sato M, Takagi H, Hasegawa T, Kozakura Y, Yokoi H, Ohashi H, Tsuchimoto K, Hashimoto R, Fukushi S, Uda A,Muramatsu M, Takayama K, Maeda K, Takahashi Y, Nagase T, Watashi K. Antiviral Res. 2024 Oct:230:105992. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105992. - Molecular evolutionary analysis of novel NSP4 mono-reassortant G1P[8]-E2 rotavirus strains that caused a discontinuous epidemic in Japan in 2015 and 2018.
Fujii Y, Tsugawa T, Fukuda Y, Adachi S, Honjo S, Akane Y, Kondo K, Sakai Y, Tanaka T, Sato T, Higasidate Y, Kubo N, Mori T, Kato S, Hamada R, Kikuchi M, Tahara Y, Nagai K, Ohara T, Yoshida M, Nakata S, Noguchi A, Kikuchi W, Hamada H, Tokutake-Hirose S, Fujimori M, Muramatsu M. Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1430557. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1430557. eCollection 2024.PMID: 39050631 . - Enterovirus 3A protein disrupts endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis through interaction with GBF1.
Hirano J, Hayashi T, Kitamura K, Nishimura Y, Shimizu H, Okamoto T, Okada K, Uemura K, Yeh MT, Ono C, Taguwa S, Muramatsu M, Matsuura Y. J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0081324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00813-24. Epub 2024 Jun 21. - Highlights from the 2023 International Meeting on the Molecular Biology of Hepatitis B virus.
HBV2023; Allweiss L, Cohen C, Dias J, Fumagalli V, Guo H, Harris JM, Hu J, Iannacone M, Isogawa M, Jeng WJ, Kim KH, Kramvis A, Li W, Lucifora J, Muramatsu M, Neuveut C, Ploss A, Pollicino T, Protzer U, Tan A, Tanaka Y, Tu T, Tsukuda S, Thimme R, Urban S, Watashi K, Yuan Z, Yeh SH, McKeating JA, Revill PA. J Gen Virol. 2024 May 16;105(5). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001978. - Loxapine inhibits replication of hepatitis A virus in vitro and in vivo by targeting viral protein 2C.
Matsuda M, Hirai-Yuki A, Kotani O, Kataoka M, Zheng X, Yamane D, Yokoyama M, Ishii K,Muramatsu M, Suzuki R. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Mar 13;20(3):e1012091. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012091. eCollection 2024 Mar. - Chimeric provirus of bovine leukemia virus/SMAD family member 3 in cattle with enzootic bovine leukosis.
Nao N, Okagawa T, Nojiri N, Konnai S, Shimakura H, Tominaga M, Yoshida-Furihata H, Nishiyama E, Matsudaira T, Maekawa N, Murata S, Muramatsu M, Ohashi K, Saito M. Arch Virol. 2024 Feb 16;169(3):47. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-05970-3.PMID: 38366081. - Generation of JC Polyoma Pseudovirus for High-Throughput Measurement of Neutralizing Antibodies.
Matsuda M, Li TC, Nakanishi A, Nakamichi K, Saito M, Suzuki T, Matsuura T, Muramatsu M, Suzuki T, Miura Y, Suzuki R. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;14(3):311. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030311.PMID: 38337826 . - Enterovirus A71 does not meet the uncoating receptor SCARB2 at the cell surface.
Nishimura Y, Sato K, Koyanagi Y, Wakita T, Muramatsu M, Shimizu H, Bergelson JM, Arita M. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Feb 15;20(2):e1012022. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012022. - Antiviral effect of peptoids on hepatitis B virus infection in cell culture.
Murayama A, Hitomi I, Yamada N, Aly HH, Molchanova N, Lin JS, Nishitsuji H, Shimotohno K, Muramatsu M, Barron AE, Kato T. Antiviral Res. 2024 Jan 23:105821. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105821. - Structural basis of hepatitis B virus receptor binding.
Asami J, Park JH, Nomura Y, Kobayashi C, Mifune J, Ishimoto N, Uemura T, Liu K, Sato Y, Zhang Z, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Drew D, Iwata S, Shimizu T, Watashi K, Park SY, Nomura N, Ohto U.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Mar;31(3):447-454. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01191-5. Epub 2024 Jan 17.PMID: 38233573.
2023
- A versatile method to profile hepatitis B virus DNA integration.
Kento Fukano, Kousho Wakae, Naganori Nao, Masumichi Saito, Akihito Tsubota, Takae Toyoshima, Hideki Aizaki, Hiroko Iijima, Takahiro Matsudaira, Moto Kimura, Koichi Watashi, Wataru Sugiura, Masamichi Muramatsu(#). Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 2023 Dec 1;7(12):e0328. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000328. - Hepatoviruses promote very-long-chain fatty acid and sphingolipid synthesis for viral RNA replication and quasi-enveloped virus release.
Shiota T, Li Z, Chen GY, McKnight KL, Shirasaki T, Yonish B, Kim H, Fritch EJ, Sheahan TP, Muramatsu M, Kapustina M, Cameron CE, Li Y, Zhang Q, Lemon SM. Sci Adv. 2023 Oct 20;9(42):eadj4198. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj4198. - Viral protease cleavage of MAVS in genetically modified mice with hepatitis A virus infection.
Sun L, Feng H, Misumi I, Shirasaki T, Hensley L, González-López O, Shiota I, Chou WC, Ting JP, Cullen JM, Cowley DO, Whitmire JK, Lemon SM. J Hepatol. 2023 Feb;78(2):271-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.013. Epub 2022 Sep 22. PubMed PMID: 36152761. - Neutralizing activity of intravenous immune globulin products against enterovirus D68 strains isolated in Japan.
Yoshida K, Muramatsu M, Shimizu H. BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 18;23(1):481. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08429-z.PMID: 37464326. - Selective inhibition of hepatitis B virus internalization by oxysterol derivatives.
Oshima M, Stappenbeck F, Ohashi H, Iwamoto M, Fukano K, Kusunoki A, Zheng X, Wang F, Morishita R, Aizaki H, Suzuki R, Muramatsu M, Kuramochi K, Sureau C, Parhami F, Watashi K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jul 13;675:139-145. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.07.014.: 37473528. - Nationwide epidemiologic epidemiologic and genetic surveillance of hepatitis E in Japan, 2014-2021.
Sugiyama R, Takahara O, Yahata Y, Kanou K, Nagashima M, Kiyohara T, Li TC, Arima Y, Shinomiya H, Ishii K, Muramatsu M, Suzuki R. J Med Virol. 2023 Jun;95(6):e28886. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28886.PMID: 37350032. - Inhibitory effect of Ephedra herba on human norovirus infection in human intestinal organoids.
Hayashi T, Murakami K, Ando H, Ueno S, Kobayashi S, Muramatsu M, Tanikawa T, Kitamura M. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jun 2;671:200-204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.05.127. Online ahead of print.PMID: 37302295. - Performance evaluation of in vitro diagnostic kits for hepatitis B virus infection using the regional reference panel of Japan.
Momose H, Murayama A, Yamada N, Matsubayashi K, Matsuoka S, Ikebe E, Kuramitsu M, Muramatsu M, Kato T, Hamaguchi I. Virol J. 2023 May 10;20(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02054-7.PMID: 37165426. - Hepatocellular organellar abnormalities following elimination of hepatitis C virus.
Aoyagi H, Iijima H, Gaber ES, Zaitsu T, Matsuda M, Wakae K, Watashi K, Suzuki R, Masaki T, Kahn J, Saito T, El-Kassas M, Shimada N, Kato K, Enomoto M, Hayashi K, Tsubota A, Mimata A, Sakamaki Y, Ichinose S, Muramatsu M, Wake K, Wakita T, Aizaki H. Liver Int. 2023 Jun 13. doi: 10.1111/liv.15624. Online ahead of print.PMID: 37312620. - Open Reading Frame 4 Is Not Essential in the Replication and Infection of Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus.
Bai H, Ami Y, Suzaki Y, Doan YH, Muramatsu M, Li TC. Viruses. 2023 Mar 18;15(3):784. doi: 10.3390/v15030784.PMID: 36992492. - Distribution of Human Sapovirus Strain Genotypes over the last four Decades in Japan: a Global Perspective.
Doan YH, Yamashita Y, Shinomiya H, Motoya T, Sakon N, Suzuki R, Shimizu H, Shigemoto N, Harada S, Yahiro S, Tomioka K, Sakagami A, Ueki Y, Komagome R, Saka K, Okamoto-Nakagawa R, Shirabe K, Mizukoshi F, Arita Y, Haga K, Katayama K, Kimura H, Muramatsu M, Oka T. Jpn J Infect Dis.2023 Mar 31. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2022.704. - Amentoflavone inhibits hepatitis B virus infection via the suppression of preS1 binding to host cells.
Aoki-Utsubo C, Indrasetiawan P, Fukano K, Muramatsu M, Artanti N, Hanafi M, Hotta H, Kameoka M. Microbiol Immunol. 2023 Mar 16. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13064. - Androgen promotes squamous differentiation of atypical cells in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia via an ELF3-dependent pathway.
Matsumoto T, Suzuki T, Nakamura M, Yamamoto M, Iizuka T, Ono M, Kagami K, Kasama H, Kanda T, Sakai Y, Iwadare J, Matsuoka A, Kayahashi K, Wakae K, Muramatsu M, Kyo S, Yamamoto Y, Mizumoto Y, Daikoku T, Fujiwara H. Cancer Med. 2023 Mar 23. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5824. - Seroepidemiology of hepatitis A virus infection in Japan: An area of very low endemicity.Kiyohara T, Ishii K, Satake M, Matsubayashi K, Suzuki R, Sugiyama R, Sunagawa T, Muramatsu M.
Microbiol Immunol. 2023 Jan;67(1):14-21. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13035.
2022
- Genetic Characterization of Human Rabies Vaccine Strain in Japan and Rabies Viruses Related to Vaccine Development from 1940s to 1980s.
Horiya M, Posadas-Herrera G, Takayama-Ito M, Yamaguchi Y, Iizuka-Shiota I, Kato H, Okamoto A, Saijo M, Lim CK. Viruses. 2022 Sep 29;14(10). doi: 10.3390/v14102152. PubMed PMID: 36298707; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9607234. - The ZCCHC14/TENT4 complex is required for hepatitis A virus RNA synthesis.
Li Y, Misumi I, Shiota T, Sun L, Lenarcic EM, Kim H, Shirasaki T, Hertel-Wulff A,Tibbs T, Mitchell JE, McKnight KL, Cameron CE, Moorman NJ, McGivern DR, Cullen JM,Whitmire JK, Lemon SM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 12;119(28):e2204511119. - Nonlytic Quasi-Enveloped Hepatovirus Release Is Facilitated by pX Protein Interaction with the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase ITCH.
Shirasaki T, González-López O, McKnight KL, Xie L, Shiota T, Chen X, Feng H, Lemon SM. J Virol. 2022 Nov 9;96(21):e0119522. - FOXP4 inhibits squamous differentiation of atypical cells in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia via an ELF3-dependent pathway.
Matsumoto T, Iizuka T, Nakamura M, Suzuki T, Yamamoto M, Ono M, Kagami K, Kasama H, Wakae K, Muramatsu M, Horike SI, Kyo S, Yamamoto Y, Mizumoto Y, Daikoku T, Fujiwara H. Cancer Sci.
2022 Oct;113(10):3376-3389. doi: 10.1111/cas.15489. Epub 2022 Aug 1.PMID: 35838233. - Identification of neutralizing epitopes in the preS2 domain of the hepatitis B virus.
Yato K, Matsuda M, Fukano K, Tanaka T, Moriishi K, Nishitsuji H, Shimotohno K, Tamura K, Wakita T, Muramatsu M, Kato T, Suzuki R. Virus Res. 2023 Jan 2;323:199014. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.199014. Epub 2022 Nov 26.PMID: 36511290. - Characterization of a Human Sapovirus Genotype GII.3 Strain Generated by a Reverse Genetics System: VP2 Is a Minor Structural Protein of the Virion.
Li TC, Kataoka M, Doan YH, Saito H, Takagi H, Muramatsu M, Oka T. Viruses. 2022 Jul 27;14(8):1649. doi: 10.3390/v14081649.PMID: 36016271. - Independent evolution of multi-dominant viral genome species observed in a hepatitis C virus carrier.
Ando T, Aizaki H, Sugiyama M, Date T, Hayashi K, Ishigami M, Katano Y, Goto H, Mizokami M, Muramatsu M, Kuroda M, Wakita T. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Aug 29;32:101327. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101327. eCollection 2022 Dec.PMID:36072891. - Macrophage Depletion Reactivates Fecal Virus Shedding following Resolution of Acute Hepatitis A in Ifnar1-/- Mice.
Shiota T, Matsuda M, Zheng X, Nagata N, Ishii K, Suzuki R, Muramatsu M, Takimoto K, Hanaki KI, Lemon SM, McGivern DR, Hirai-Yuki A. J Virol. 2022 Nov 10:e0149622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01496-22. Online ahead of print.PMID: 36354341 - Neutralization of hepatitis B virus with vaccine-escape mutations by hepatitis B vaccine with large-HBs antigen.
Washizaki A, Murayama A, Murata M, Kiyohara T, Yato K, Yamada N, Aly HH, Tanaka T, Moriishi K, Nishitsuji H, Shimotohno K, Goh Y, Ishii KJ, Yotsuyanagi H, Muramatsu M, Ishii K, Takahashi Y, Suzuki R, Akari H, Kato T. Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 5;13(1):5207. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32910-z.PMID: 36064848. - Interferon-alpha responsible EPN3 regulates hepatitis B virus replication.
Li X, Wang Z, Zhou W, Fu X, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Yang B, Bai Y, Dai C, Xu X, Cui F, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Wang B, Li Y, Muramatsu M, Wakae K, Liu G. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:944489. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.944489. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35935763. - Prediction of hand, foot, and mouth disease epidemics in Japan using a long short-term memory approach.
Yoshida K, Fujimoto T, Muramatsu M, Shimizu H. PLoS One. 2022 Jul 28;17(7):e0271820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271820. eCollection 2022.PMID: 35900968. - Isolation and genome sequencing of hepatitis E virus genotype 1 imported from India to Japan.
Kobayashi S, Mori A, Sugiyama R, Li TC, Fujii Y, Yato K, Matsuda M, Shiota T, Katsumata M, Iwamoto T, Muramatsu M, Suzuki R . Jpn J Infect Dis. 2022 Jun 30. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2022.127. Online ahead of print.PMID: 35768276. - Fungal Secondary Metabolite Exophillic Acid Selectively Inhibits the Entry of Hepatitis B and D Viruses.
Kobayashi C, Watanabe Y, Oshima M, Hirose T, Yamasaki M, Iwamoto M, Iwatsuki M, Asami Y, Kuramochi K, Wakae K, Aizaki H, Muramatsu M, Sureau C, Sunazuka T, Watashi K. Viruses. 2022 Apr 6;14(4):764. doi: 10.3390/v14040764. - Novel Neplanocin A Derivatives as Selective Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus with a Unique Mechanism of Action.
Toyama M, Watashi K, Ikeda M, Yamashita A, Okamoto M, Moriishi K, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Sharon A, Baba M. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jun 21;66(6):e0207321. doi: 10.1128/aac.02073-21. Epub 2022 May 23. - Evaluation of Heat Inactivation of Human Norovirus in Freshwater Clams Using Human Intestinal Enteroids.
Hayashi T, Yamaoka Y, Ito A, Kamaishi T, Sugiyama R, Estes MK, Muramatsu M, Murakami K. Viruses. 2022 May 10;14(5):1014. doi: 10.3390/v14051014. - Estrogen induces the expression of EBV lytic protein ZEBRA, a marker of poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Dochi H, Kondo S, Murata T, Fukuyo M, Nanbo A, Wakae K, Jiang WP, Hamabe-Horiike T, Tanaka M, Nishiuchi T, Mizokami H, Moriyama-Kita M, Kobayashi E, Hirai N, Komori T, Ueno T, Nakanishi Y, Hatano M, Endo K, Sugimoto H, Wakisaka N, Juang SH, Muramatsu M, Kaneda A, Yoshizaki T. Cancer Sci. 2022 May 28. doi: 10.1111/cas.15440. Online ahead of print. - RAISING is a high-performance method for identifying random transgene integration sites.
Wada Y, Sato T, Hasegawa H, Matsudaira T, Nao N, Coler-Reilly ALG, Tasaka T, Yamauchi S, Okagawa T, Momose H, Tanio M, Kuramitsu M, Sasaki D, Matsumoto N, Yagishita N, Yamauchi J, Araya N, Tanabe K, Yamagishi M, Nakashima M, Nakahata S, Iha H, Ogata M, Muramatsu M, Imaizumi Y, Uchimaru K, Miyazaki Y, Konnai S, Yanagihara K, Morishita K, Watanabe T, Yamano Y, Saito M. Commun Biol. 2022 Jun 2;5(1):535. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03467-w. - Significant role of host sialylated glycans in the infection and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Saso W, Yamasaki M, Nakakita SI, Fukushi S, Tsuchimoto K, Watanabe N, Sriwilaijaroen N, Kanie O, Muramatsu M, Takahashi Y, Matano T, Takeda M, Suzuki Y, Watashi K. PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jun 14;18(6):e1010590. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010590. eCollection 2022 Jun.PMID: 35700214. - Novel flavonoid hybrids as potent antiviral agents against hepatitis A: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation.
Shi S, Zheng X, Suzuki R, Li Z, Shiota T, Wang J, Hirai-Yuki A, Liu Q, Muramatsu M(#), Song SJ(#). Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Aug 5;238:114452. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114452. Epub 2022 May 14.PMID: 35597006. - Mongolia Gerbils Are Broadly Susceptible to Hepatitis E Virus.
Zhang W, Ami Y, Suzaki Y, Doan YH, Muramatsu M, Li TC. Viruses. 2022 May 24;14(6):1125. doi: 10.3390/v14061125. - Structural insights into the bile acid transporter NTCP, the receptor for HBV.
Jae-Hyun Park, Masashi Iwamoto, Ji-Hye Yun, Tomomi Uchikubo-Kamo, Donghwan Son, Zeyu Jin1, Hisashi Yoshida, Mio Ohki, Naito Ishimoto, Kenji Mizutani, Mizuki Oshima, Masamichi Muramatsu, Takaji Wakita, Mikako Shirouzu, Kehong Liu, Tomoko Uemura, Norimichi Nomura, So Iwata, Koichi Watashi, Jeremy R. H. Tame, Tomohiro Nishizawa, Weontae Lee, Sam-Yong Park. Nature. 2022 Jun;606(7916):1027-1031.doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04857-0. - The kinesin KIF4 mediates HBV/HDV entry through the regulation of surface NTCP localization and can be targeted by RXR agonists in vitro.
Gad SA, Sugiyama M, Tsuge M, Wakae K, Fukano K, Oshima M, Sureau C, Watanabe N, Kato T, Murayama A, Li Y, Shoji I, Shimotohno K, Chayama K, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Nozaki T, Aly HH. PLoS Pathog. 2022 Mar 21;18(3):e1009983. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009983. eCollection 2022 Mar. - Interferon-gamma induced APOBEC3B contributes to Merkel cell polyomavirus genome mutagenesis in Merkel cell carcinoma.
Que L, Li Y, Dainichi T, Kukimoto I, Nishiyama T, Nakano Y, Shima K, Suzuki T, Sato Y, Horike S, Aizaki H, Watashi K, Kato T, Aly HH, Watanabe N, Kabashima K, Wakae K(#), Muramatsu M(#). J Invest Dermatol. 2022, Jul;142(7):1793-1803.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.12.019. - Activities of endogenous APOBEC3s and uracil-DNA-glycosylase affect the hypermutation frequency of hepatitis B virus cccDNA
Kouichi Kitamura , Kento Fukano , Lusheng Que , Yingfang Li, Kousho Wakae , Masamichi Muramatsu. J Gen Virol. 2022 Apr;103(4). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001732. - Development of an intervention system for linkage-to-care and follow-up for hepatitis B and C virus carriers.
Kikuchi M, Sawabe M, Aoyagi H, Wakae K, Watashi K, Hattori S, Kawabe N, Yoshioka K, Tanaka J, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Aizaki H. Hepatol Int. 2022 Feb;16(1):68-80. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10269-5. Epub 2021 Dec 2. - Induction of neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus by a subviral particle-based DNA vaccine.
Yato K, Matsuda M, Watanabe N, Watashi K, Aizaki H, Kato T, Tamura K, Wakita T, Muramatsu M, Suzuki R. Antiviral Res. 2022 Feb 20;199:105266. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105266. PMID: 35196560. - Experimental Cross-Species Transmission of Rat Hepatitis E Virus to Rhesus and Cynomolgus Monkeys.
Yang F, Li Y, Li Y, Jin W, Duan S, Xu H, Zhao Y, He Z, Ami Y, Suzaki Y, Doan YH, Takeda N, Zhang W, Muramatsu M, Li TC. Viruses. 2022 Jan 29;14(2):293. doi:10.3390/v14020293. - Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced ROS/JNK signaling pathway activates the E3 ubiquitin ligase Itch to promote the release of HCV particles via polyubiquitylation of VPS4A.
Deng L, Liang Y, Ariffianto A, Matsui C, Abe T, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Maki M, Shibata H, Shoji I. J Virol. 2022 Jan 19:JVI0181121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01811-21. Online ahead of print.PMID: 35044214.
