Aberrant EVI1 splicing contributes to EVI1-rearranged leukemia
Summary
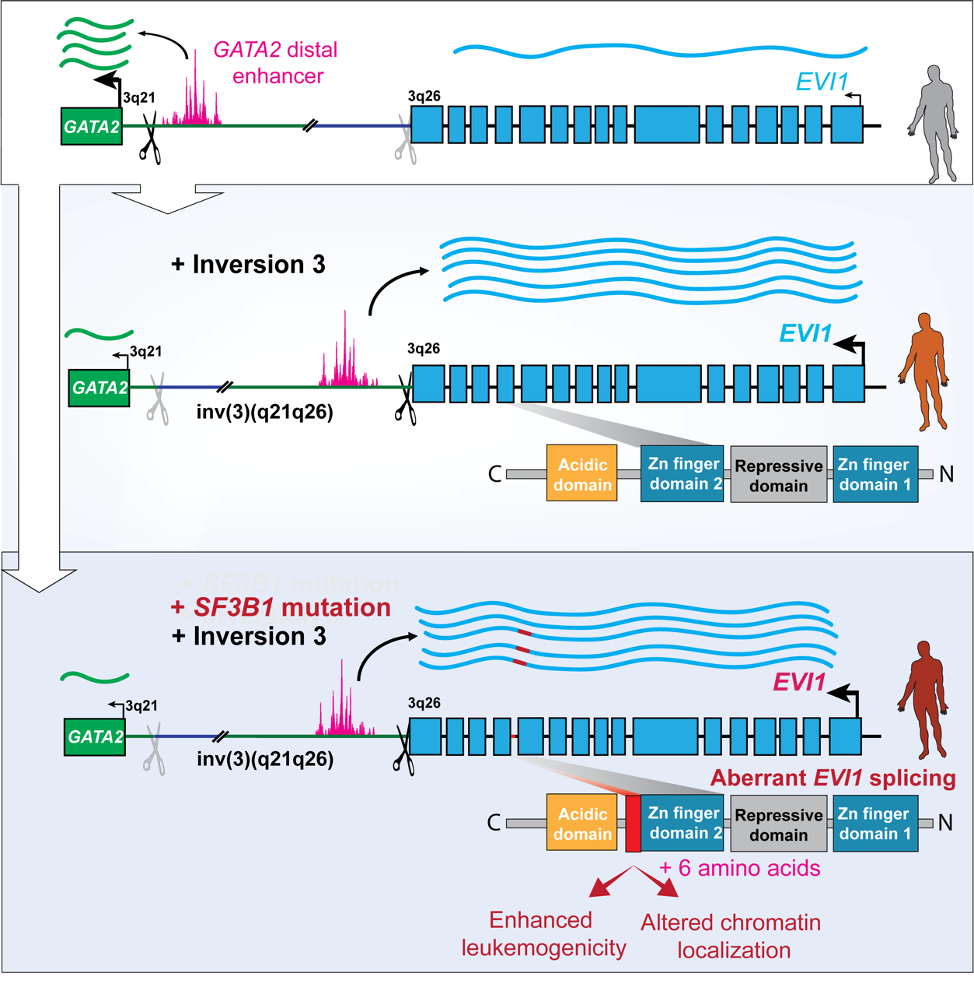
- ・A novel EVI1 splice isoform is frequently expressed in poor-prognostic leukemia harboring inv(3)/t(3;3) and drives myeloid transformation.
- ・Frequent SF3B1 mutations in inv(3)/t(3;3) leukemia generate a novel EVI1 isoform with an altered second Zinc finger DNA-binding domain.
- ・These results explain the reason why splicing factor SF3B1 mutation is very frequently mutated in inv(3)/t(3;3) leukemia
The main points are discussed in Twitter(@DaichiInoue5)
1 Research Paper
Authors:
Atsushi Tanaka1,2, Taizo A. Nakano3, Masaki Nomura1,4, Hiromi Yamazaki1, Jan P. Bewersdorf5, Roger Mulet-Lazaro6,7, Simon Hogg5, Bo Liu5, Alex Penson5, Akihiko Yokoyama8, Weijia Zang1,9, Marije Havermans6,7, Miho Koizumi10, Yasutaka Hayashi1, Hana Cho5, Akinori Kanai11,12, Stanley C. Lee13,14, Muran Xiao1,15, Yui Koike1, Yifan Zhang1,9, Miki Fukumoto1, Yumi Aoyama1,9, Tsuyoshi Konuma16, Hiroyoshi Kunimoto17, Toshiya Inaba11, Hideaki Nakajima17, Hiroaki Honda10, Hiroshi Kawamoto2, Ruud Delwel6,7, Omar Abdel-Wahab5,*, Daichi Inoue1,*
Affiliations:
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation, Foundation for Biomedical Research and Innovation at Kobe, Kobe, Hyogo, Japan.
- 2Laboratory of Immunology, Institute for Frontier Life and Medical Sciences, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Section of Hematology, Oncology and Bone Marrow Transplantation, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, United States.
- 4Facility for iPS Cell Therapy, CiRA Foundation, Kyoto, Japan.
- 5Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States.
- 6Department of Hematology, Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
- 7Oncode Institute, Utrecht, the Netherlands.
- 8Tsuruoka Metabolomics Laboratory, National Cancer Center, Yamagata, Japan.
- 9Department of Hematology and Oncology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan.
- 10Field of Human Disease Models, Major in Advanced Life Sciences and Medicine, Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Tokyo, Japan.
- 11Department of Molecular Oncology and Leukemia Program Project, Research Institute for Radiation Biology and Medicine, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan.
- 12Department of Computational Biology and Medical Sciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
- 13Clinical Research Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA, United States.
- 14Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States.
- 15Division of Cellular Therapy, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
- 16Structural Epigenetics Laboratory, Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan.
- 17Department of Stem Cell and Immune Regulation, Graduate School of Medicine, Yokohama City University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan.
Title of original: Aberrant EVI1 splicing contributes to EVI1-rearranged leukemia
Journal: Blood
doi: 10.1182/blood.2021015325.
Authors
Atushi Tanaka

PhD Student, Department of Hematology-Oncology, Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation, Foundation for Biomedical Research and Innovation at Kobe
Daichi Inoue

Professor, Department of Hematology-Oncology, Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation, Foundation for Biomedical Research and Innovation at Kobe
Inoue Lab
URL: https://www.fbri-kobe.org/english/laboratory/research5